Lasers and aesthetic procedures
Aesthetic procedures are
getting more and more popular as technology advances and more people search for
less invasive ways to look youthful and pretty. Aesthetic procedures like Botox
injections, chemical peels, dermal fillers and micro-dermabrasion will be
described after laser treatments below.
Extrinsic environmental
factors e.g. sun exposure may accelerate the ageing of skin and cause skin pigmentations, benign vascular lesions (erythema, cherry angiomas, and
telangiectasia), wrinkles and laxity of skin.
Laser stands for Light
Amplification Stimulated Emission Radiation. Laser photo rejuvenation targets
the affected lesions and leaving the normal skin unharmed. It targets the
melanin chromophore found in the pigmented lesions and the oxyhemoglobin chromophore in vascular
lesions. A few sessions need to be conducted before results can be seen.
Laser treatment is
generally safe and must be done by a well-trained physician. Eye shields should
be worn by the clinician and patient. Inflammable materials should not be
placed in the room. The room should not be accessible to outsiders when
procedure is in progress.
Adverse effects of laser
treatment include temporary reddening, blistering, bruising and burning of the
skin involved, pigmentation changes (brown or white) which maybe permanent,
infections (very low chance), scars(rarely).
There are several lasers
used in aesthetic dermatologic procedures. The different types of laser
treatments with different wavelengths which are as follows:
Carbon Dioxide Laser
-It consists of
wavelength 10600 nm
-It can be used on
recalcitrant warts,
syringomas (benign sweat duct tumors), sebaceous hyperplasia (enlarged sweat
glands), angiofibromas (benign fibrous tissues papules), trichoepitheliomas
(small benign tumor arising from hair follicle), epidermal nevus (discolored congenital birthmark), melanocytic nevi (congenital pigmented birthmark), large keloids
(fibrous scar tissue post trauma/injury), scars and wrinkles.
Q switched Nd YAG laser
-It consists of
wavelength 532 nm and 1064 nm
-It can be used for solar lentigines (brown pigment because of ageing), freckles, tattoos
and nevus of Ota (congenial pigmented birthmark).
Pulsed dye laser
-It consists of
wavelength 59 nm
-It can be used for
hemangioma of infancy (benign blood vessels tumor), portwine stain (ruby red
birthmark), face and leg telangiectasia (dilatation of small blood vessels), Poikiloderma
(mottling pigmentation disorder), keloids (fibrous scar tissue) and striae
(stretch marks).
Long pulsed Nd YAG laser
-It consists of 1064 nm
-It can be used for hair
removal.
Non ablative diode laser
-It consists of 1540nm
wavelength
-It can be used for
superficial scars, wrinkles
Intense Pulse Light
-It consists of 400-1200
nm wavelengths
-It can be used for
freckles, facial telangiectasia (dilatation of small blood vessels) and hair
removal.
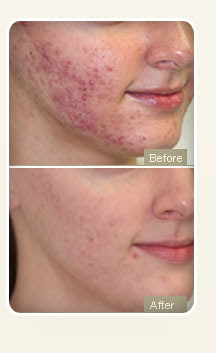
Fractional ablative carbon dioxide laser
-It consists of 10600 nm
wavelength
-It can be used for
wrinkles, acne scars and photo-damaged skin.
Derma-Radiofrequency
-The radiofrequency
penetrates to deeper skin layers and bounce off to the subcutaneous layer as
heat resulting in skin tightening. It is more for skin rejuvenation.
Botox Injections
Botulinum toxin is a
potent neurotoxin from the bacteria clostridium Botulinum. The neurotoxin
inhibits acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction which causes
temporary denervation.
Botox injections are purified
forms of the neurotoxin. Botox injections into specific facial muscles will
result in relaxation of these muscles with overall smoothening of skin and
wrinkle reductions.
Botox injections are
also used for other medical conditions like hyperhidrosis,
strabismus, cervical dystonia, muscle spasticity and blepharospasm.
Now Botox injections are
used commonly to smooth out frown lines, crow feet, forehead furrows and skin
bands on neck. Treatment can be done every 3-4 months. It is a very fast
procedure.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peel is a form
of chemical exfoliation of the skin. The agents used are alpha hydroxy acids
(e.g., glycolic and lactic acids) and beta hydroxy acids (e.g., salicylic
acid). By wounding and removing the superficial skin layers with the chemicals,
it stimulates skin to renew, increase skin hydration and regenerate new
healthier epidermis and dermis.
Chemical peels are used
mainly on the face to improve age spots, acne scars, wrinkles,
freckles, rough skin patches, sun-damaged skin and irregular skin pigmentation.
Chemical peels may be
done up to 6 times per month and thereafter monthly for maintenance. The
results only last for a short term. Side effects are skin peeling post
procedure, risks of hyper-pigmentation/ hypo-pigmentation and scarring with
deeper peels.
Derma Fillers
Dermal fillers are
injectable substances used for facelift by adding volume to sagged areas on the
face. In 1980s Bovine collagens are the first injectable fillers used; it can
only last for 3-4 months. The newer fillers that contain Hyaluronic acid now
can last from 6 to 12 months.
Dermal fillers
injections’ results are dependent on the physician skills. It can be used to
plump up lips and smooth out wrinkles and folds over the lower 2/3 of the face.
The interval between the injections depends on how long the effects last. Side
effects include post-procedure bruising and swelling.
Micro-dermabrasion
Micro-dermabrasion is a
form of mechanical exfoliation of the skin with a refined abrasive
element/instrument to sand the skin and remove the superficial skin layer. This
will thicken your collagen and also stimulate renewal and regenerate new skin
layers.
It can be used to treat
superficial scars, wrinkles, large pores, acne, acne scars and
age spots. Few sessions can be conducted every 2 to 4 weeks and with subsequent
monthly maintenance. The results are short term like chemical peels. A single
session may not produce satisfactory effect. The side effects include redness
post procedure and worsening of telangiectasia (dilatation of small blood
vessels).
















No comments:
Post a Comment